State Choices to Promote Access
- 49 states and the District of Columbia set the income eligibility limit for public health insurance (Medicaid/SCHIP) at or above 200% of the federal poverty level (FPL) for children ages birth to 5. [2016]2
- 34 states set the income eligibility limit for public health insurance (Medicaid/SCHIP) at or above 200% of the federal poverty level (FPL) for pregnant women. [2016]2
- 12 states set the income eligibility limit for public health insurance (Medicaid/SCHIP) at or above 200% of the federal poverty level (FPL) for immigrant children 0-1yr. [2016]2
- 6 states set the income eligibility limit for public health insurance (Medicaid/SCHIP) at or above 200% of the federal poverty level (FPL) for immigrant children 3-5yrs. [2016]2
- 18 states set the income eligibility limit for public health insurance (Medicaid/SCHIP) at or above 200% of the federal poverty level (FPL) for immigrant pregnant women. [2016]2
- 28 states [2014]3
- 23 states [2014]3
- 30 states provides temporary coverage to pregnant women under Medicaid until eligibility can be formally determined [2018]4
- 20 states provides temporary coverage to children under Medicaid or CHIP until eligibility can be formally determined [2018]4
- 6 states includes at-risk children in the definition of eligibility for IDEA Part C [2014]5
- 32 states does not require redetermination of eligibility for Medicaid/CHIP more than once a year [2018]4
- 33 states has adopted Medicaid expansion as part of the Affordable Care Act [2018]6
State Choices to Promote Quality
EPSDT screening periodicity schedule meets recommendations of American Academy of Pediatrics [FY 2016]7
- 18 states 7 screenings for children <1 year
- 45 states 4 screenings for children 1-2 years
- 51 states 3 screenings for children 3-5 years
- 33 states 4 screenings for children 6-9 years
- 8 states requires newborn screening for the 31 metabolic deficiencies/disorders and core conditions [2014]8
Data Notes and Sources
Last Updated: October 29, 2015
Send us recent developments to update your state's profile.
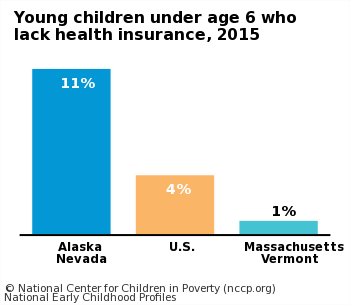
- National data were calculated from the 2011 American Community Survey, representing information from 2011. State data were calculated from the 2009-2011 American Community Survey, representing information from the years 2009 to 2011.
- Brooks, T., Miskell, S., Artiga, S., Cornachione, E., & Gates, A. (2016). Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility, Enrollment, Renewal, and Cost-Sharing Policies as of January 2016: Findings from a 50-State Survey. Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured, The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. Http://files.kff.org (accessed February 29, 2016).
- Medicaid. 2014. Medicaid and CHIP Coverage of Lawfully Residing Children and Pregnant Women. http://medicaid.gov (accessed August 25, 2015).
- Brooks, T., Miskell, S., Artiga, S., Cornachione, E., & Gates, A. (2018). Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility, Enrollment, Renewal, and Cost-Sharing Policies as of January 2018: Findings from a 50-State Survey. Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured, The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. http://files.kff.org (accessed July 2, 2018).
- Ringwalt, S. (Comp.). (2015). Summary table of states' and territories' definitions of/criteria for IDEA Part C eligibility. http://www.nectac.org (accessed August 25, 2015).
- Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured. (2018). Status of State Action on the Medicaid Expansion Decision. https://www.kff.org (accessed July 13, 2018).
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2017). The Annual EPSDT Report (Form CMS-416) for FY 2016. https://www.medicaid.gov (accessed December 11, 2017). Data were not reported for ND.
- National Newborn Screening and Genetics Resource Center. 2014. National Newborn Screening Status Report. http://genes-r-us.uthscsa.edu (accessed March 24, 2015).