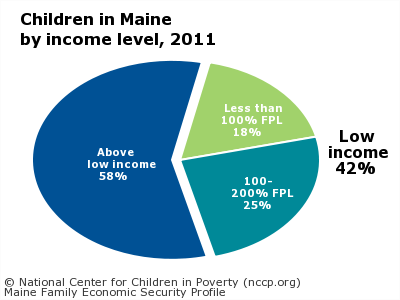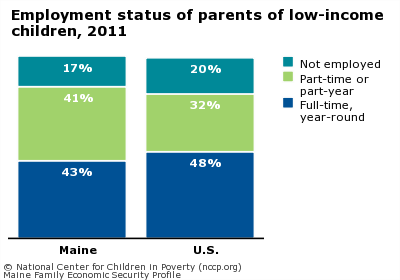| Overview | Work Attachment and Advancement |
State policies that promote the economic security of our nation’s families can help offset larger economic and social conditions that make it difficult for families to get by and get ahead. This four-part profile provides data on Maine’s low-income children and families and highlights state policy choices regarding families’ work attachment and advancement, income adequacy, and asset development.
In Maine, there are 153,394 families, with 268,750 children. Among these children, 42 percent live in families that are low-income, defined as income below twice the federal poverty level (nationally, 45 percent of children live in low-income families). Young children are particularly likely to live in low-income families.
Low wages and a lack of higher education contribute to families having insufficient incomes. Nationally, 48 percent of low-income children have at least one parent who works full-time, year-round; in Maine, the figure is 43 percent.
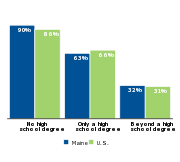
Parents without a college education often struggle to earn enough to support a family, but only 26 percent of adults in Maine have a bachelor’s degree. A substantial portion of children in Maine whose parents only have a high school diploma—63 percent—are low income.
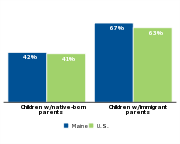
Children of foreign-born parents are also more likely to be low income than children of native-born parents.
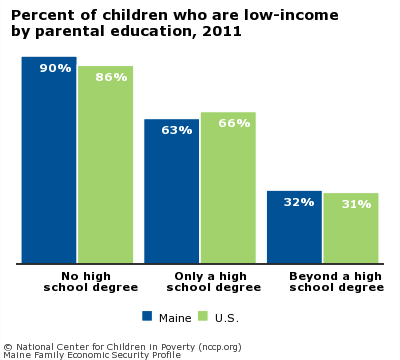
Percent of children who are low-income by parental education, 20111
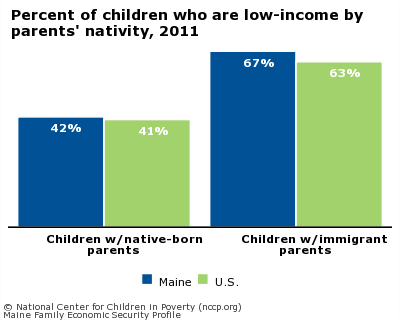
Percent of children who are low-income by parents' nativity, 20111
Learn more about Maine’s children.
| Work Attachment and Advancement |
Data Notes and Sources
Data were compiled from 50-state sources. Some state policy decisions may have changed since these data were collected.